Note
Click here to download the full example code
NeuralNet Tutorial¶
from pypose.module.dynamics import System
import torch as torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
Preparation¶
class nnDynamics(System):
def __init__(self, hiddenSize):
super().__init__()
self.net = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(2, hiddenSize[0]),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(hiddenSize[0], hiddenSize[1]),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(hiddenSize[1], 2))
def state_transition(self, state, input, t=None):
return self.net(state) + input
def observation(self, state, input, t=None):
return state
def createTimePlot(x, y, figname="Un-named plot", title=None, xlabel=None, ylabel=None):
f = plt.figure(figname)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel(xlabel)
plt.ylabel(ylabel)
plt.title(title)
return f
Time Step
dt = 0.01 # Time step size
N = 1000 # Number of time steps
Time and input
time = torch.arange(0, N + 1) * dt
input = torch.sin(time)
Initial state
state = torch.tensor([0,0])
Create solver object
nnSolver = nnDynamics([5, 10])
Calculate trajectory
state_all = torch.zeros(N + 1, 2)
state_all[0,:] = state
for i in range(N):
state_all[i+1], _ = nnSolver.forward(state_all[i], input[i])
Create plots
x, y = (state_all.T).detach().numpy()
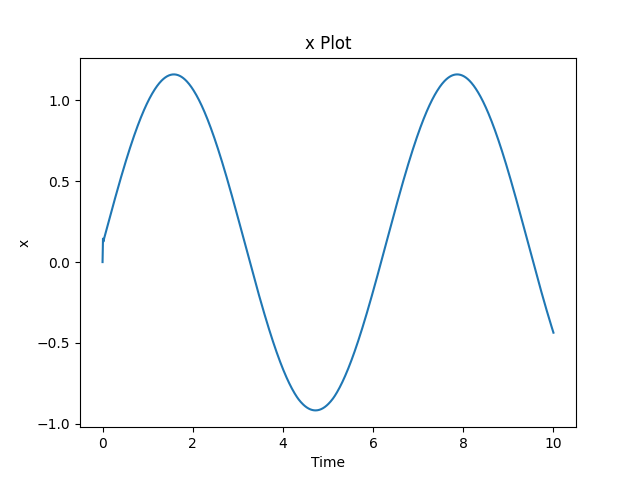
x_fig = createTimePlot(time, x, figname="x Plot", xlabel="Time", ylabel="x", title="x Plot")
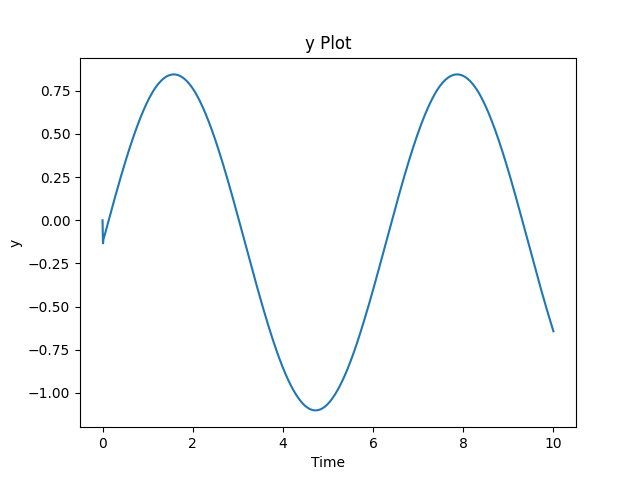
y_fig = createTimePlot(time, y, figname="y Plot", xlabel="Time", ylabel="y", title="y Plot")
# torch.save([state_all], 'nn_dynamics_data.pt')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.126 seconds)